The Mindoro Forests in the Philippines host diverse species, including many endemics, but are threatened by human activities such as deforestation and mining. Conservation efforts are underway, but urgent action is necessary to protect the remaining biodiversity. Further research and conservation measures are crucial to ensure the survival of this vital ecosystem.
In this blog post, we will explore the biodiversity and endemism of the Philippine Mindoro forests. We will discuss the importance of biodiversity and endemism in these unique habitats, examine the various species that inhabit them, consider the threats to their survival, and look at existing conservation efforts as well as future directions for research and conservation.

Importance of Biodiversity and Endemism in Mindoro Forests
The biodiversity and endemism of the Mindoro Forests are of great importance for ecological and economic reasons. Ecologically, the region’s diverse array of flora and fauna plays a vital role in maintaining the health of the forest ecosystem.
The different species, each with their own unique characteristics, interact with each other and contribute to the complex ecological processes that sustain the forest. This in turn benefits local communities and other species, such as those in neighboring ecosystems.
From an economic standpoint, the Mindoro Forests also provide significant benefits. The forests are a source of timber, non-timber forest products, and other resources that are important for local livelihoods and industries.
Additionally, the forests attract tourists interested in experiencing the unique biodiversity and cultural heritage of the region. The conservation of the biodiversity and endemism of the Mindoro Forests is therefore important not just for ecological reasons, but also for the economic well-being of local communities.
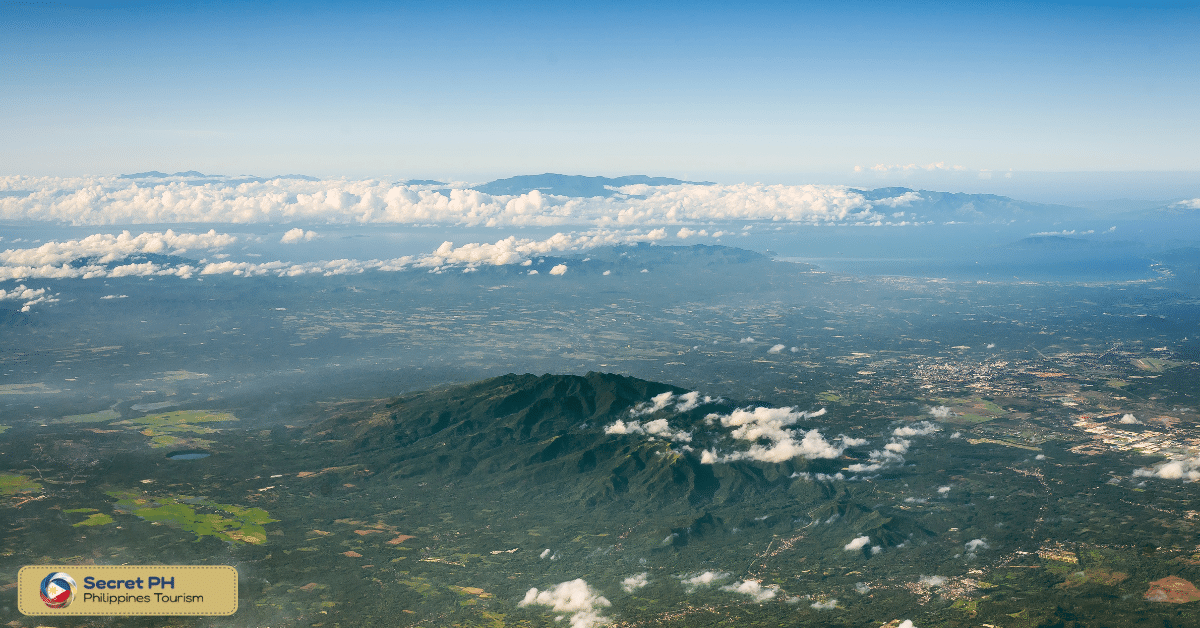

Biodiversity of Mindoro Forests
The Philippine Mindoro Forest is one of the most biodiverse areas in the world, with a rich variety of flora and fauna unique to the region. The forest, which covers a large portion of Mindoro Island in the Philippines, is known for its stunning beauty and ecological importance. In this section, we will explore the biodiversity of the Mindoro Forests and the unique species that call it home.
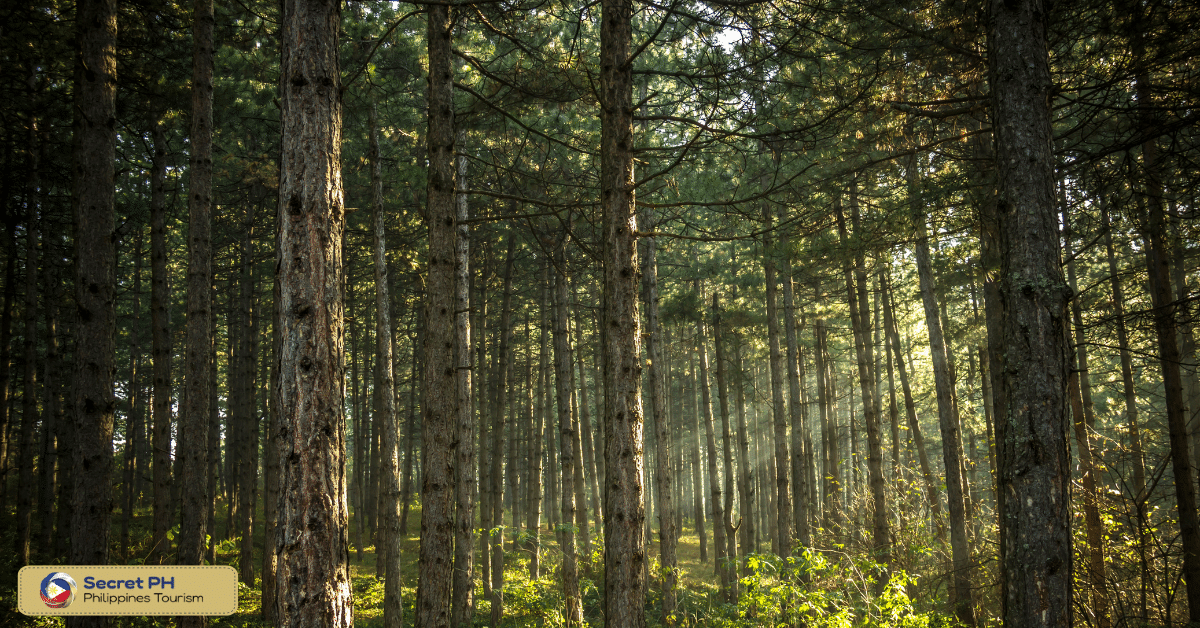
Flora
The Mindoro Forests are home to a rich and diverse flora. With an estimated 1,000 plant species, many of which are endemic to the region.
These include various species of dipterocarp trees, which are an important timber source in the Philippines. As well as rare and threatened species such as the Mindoro Pine (Pinus merkusii subsp. mindorensis) and the Mindoro Rafflesia (Rafflesia speciosa), which is one of the largest flowers in the world.
The forest also contains numerous species of orchids, ferns, and other epiphytic plants, as well as a variety of medicinal plants that are traditionally used by local communities. However, the forest is under threat due to deforestation, mining, and other forms of habitat destruction, which puts the future of these unique and valuable plant species in jeopardy.

Fauna
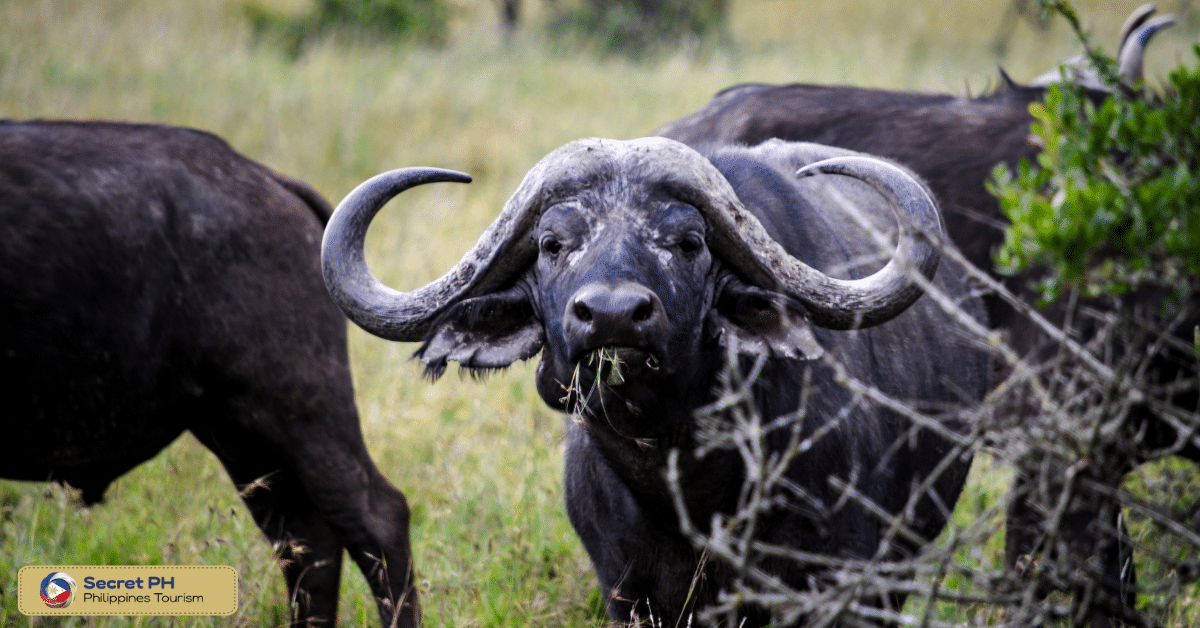
The Mindoro Forests are home to a diverse range of fauna, with many species that are endemic to the region. This includes the critically endangered Mindoro Tamaraw, Mindoro Bleeding-heart, and the Mindoro Imperial Pigeon.
The forest also supports numerous species of reptiles, amphibians, and mammals, including several species of rodents and bats. However, habitat destruction, hunting, and other forms of human activity are threatening the survival of many of these species. Making conservation efforts crucial for the preservation of the unique and valuable fauna of the Mindoro Forests.

Endemism in Mindoro Forests
Endemism refers to the ecological phenomenon of a species or group of species being restricted to a particular geographic area. Endemic species are unique to that particular region and are not found anywhere else. This is often due to the isolation of a particular geographical area, such as an island or mountain range, which creates a unique ecosystem with its own distinct set of species.
Furthermore, endemic species often play key roles in their ecosystems, such as pollinators or seed dispersers. The loss of such species can have far-reaching consequences for the health and functioning of the entire ecosystem.
There are numerous examples of endemic species in the Mindoro forest, with some of the most notable being:
Mindoro Tamaraw (Bubalus mindorensis): The Mindoro Tamaraw is a critically endangered species of water buffalo that is endemic to the island of Mindoro.
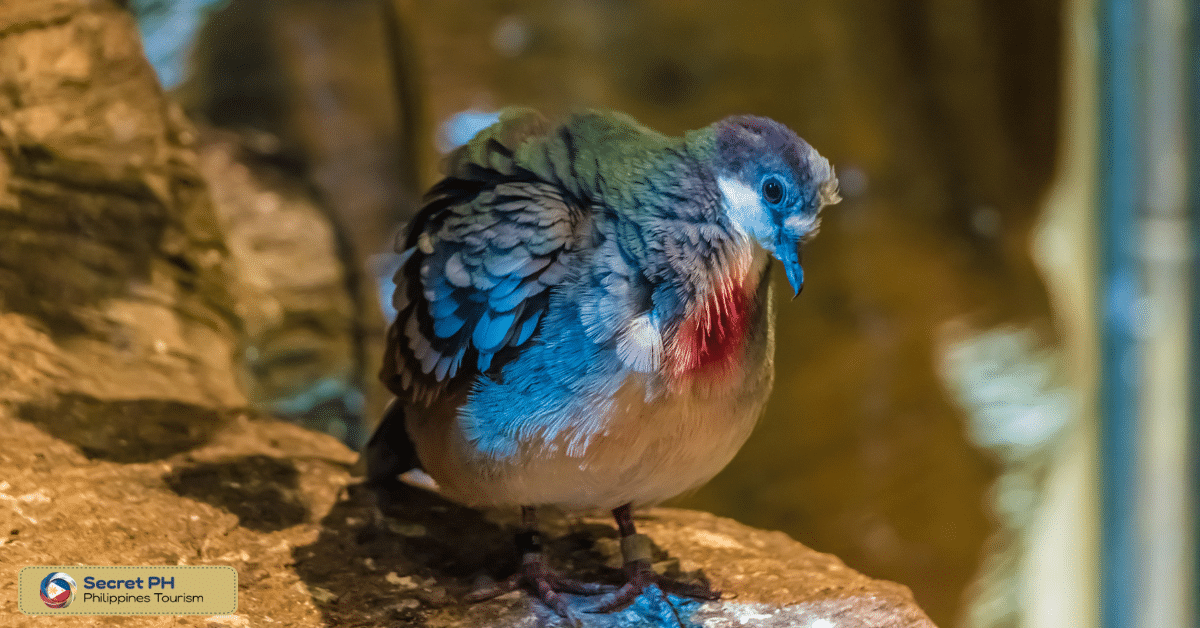
Mindoro Bleeding-heart (Gallicolumba platenae): The Mindoro Bleeding-heart is a species of dove that is endemic to Mindoro. It gets its name from the distinctive red patch on its breast.
Mindoro Imperial Pigeon (Ducula mindorensis): The Mindoro Imperial Pigeon is another species of dove that is endemic to Mindoro. They are large, colorful birds that play an important role in seed dispersal within the forest.
Mindoro Striped-babbler (Stachyris mindorensis): The Mindoro Striped-babbler is a species of bird that is endemic to Mindoro. They are small, colorful birds that are known for their distinctive striped pattern.
Mindoro Scops-owl (Otus mindorensis): The Mindoro Scops-owl is a small owl that is endemic to Mindoro. They are nocturnal birds that are known for their distinctive call.
Mindoro Forest Lizard (Pseudogekko mindorensis): The Mindoro Forest Lizard is a species of gecko that is endemic to Mindoro. They are small, nocturnal lizards that are found in the forest undergrowth.
Mindoro Climbing Rat (Cremnomys mindorensis): The Mindoro Climbing Rat is a species of rodent that is endemic to Mindoro. They are small, arboreal rodents that are found in the forest canopy.
Mindoro Striped Shrew-rat (Chrotomys mindorensis): The Mindoro Striped Shrew-rat is a species of rodent that is endemic to Mindoro. They are small, nocturnal rodents that are found in the forest undergrowth.
Mindoro Pipedragon (Celestus mindorensis): The Mindoro Pipedragon is a species of lizard that is endemic to Mindoro. They are arboreal lizards that are found in the forest canopy.
Mindoro Dwarf Buffalo (Bubalus cebuensis): The Mindoro Dwarf Buffalo is a species of water buffalo that is endemic to Mindoro. They are smaller than the Mindoro Tamaraw and are also threatened due to habitat loss and hunting.

Threats to Biodiversity in Mindoro Forests
Despite the high levels of biodiversity and endemism found in the Mindoro Forests, this region is under threat from a variety of human activities. In this section, we will explore the threats to biodiversity and endemism in the Mindoro Forests and the steps being taken to address these issues.
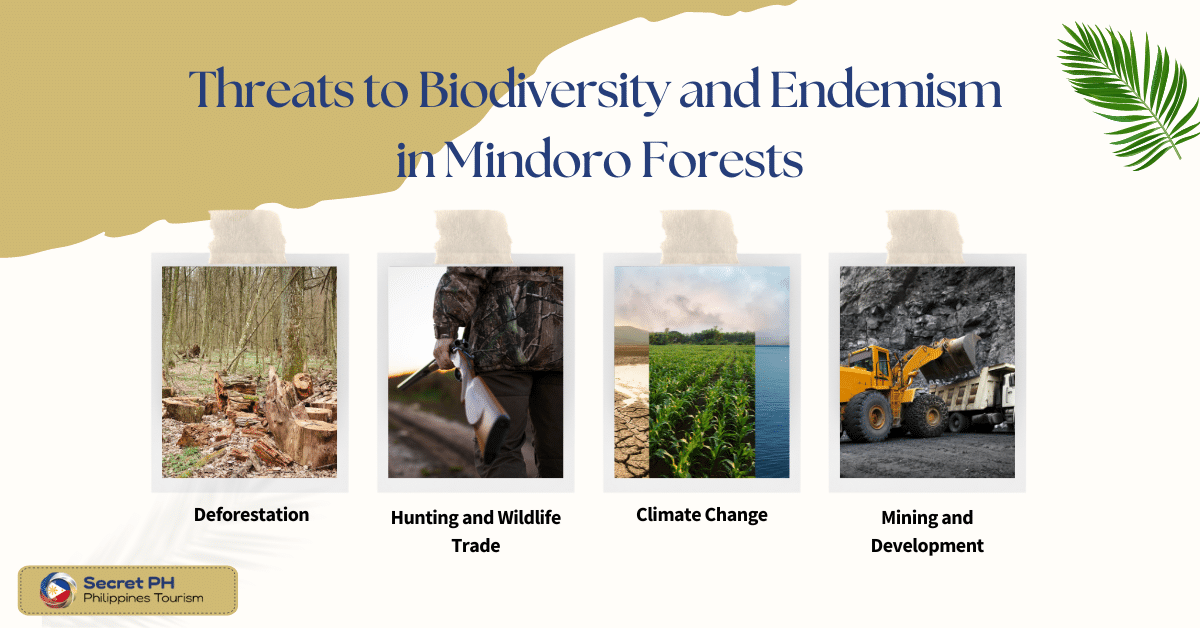
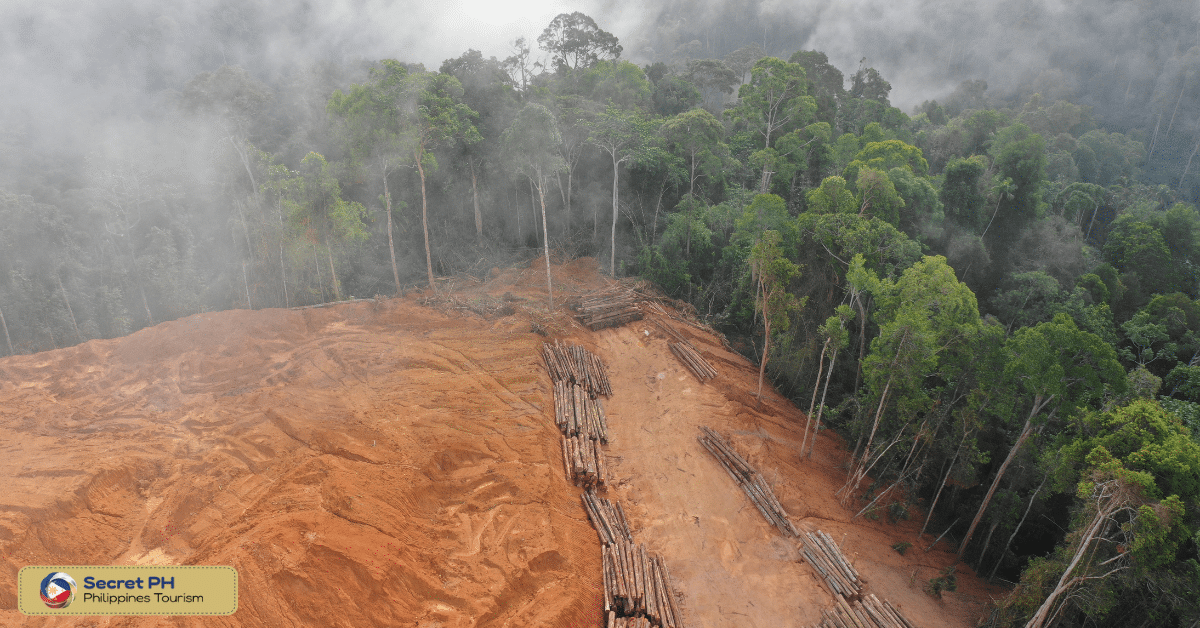
Deforestation
One of the greatest threats to biodiversity in the Mindoro Forests is deforestation. Much of the forest has been cleared for agriculture, logging, and other development activities. Deforestation not only destroys the habitat of many species but also contributes to climate change and soil erosion.
Hunting and Wildlife Trade
The Mindoro Forests are home to a number of endangered and endemic species that are hunted and traded for their meat, skins, and other body parts. This includes the critically endangered Mindoro Tamaraw, which is hunted for its meat and horns. The illegal trade in wildlife also threatens many other species in the region.
Climate Change
The effects of climate change, including rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns, pose a threat to the biodiversity of the Mindoro Forests. Changes in the environment can disrupt the delicate balance of the ecosystem and make it difficult for some species to survive.
Mining and Development
Mining and other development activities in the Mindoro Forests can have negative impacts on biodiversity and endemism. These activities can destroy the habitat of many species, disrupt ecological processes, and contribute to pollution.

Conservation Efforts for Mindoro Forests
The Mindoro Forests in the Philippines are home to a variety of endemic species and are a priority site for conservation efforts. In this section, we will explore the various conservation efforts underway in the Mindoro Forests. Including protected areas, community-based conservation programs, and reforestation efforts.
Protected Areas: One of the most important conservation efforts in the Mindoro Forests is the establishment of protected areas. These areas are designated for the conservation of biodiversity and the protection of natural resources.
Community-Based Conservation: Community-based conservation programs involve working with local communities to protect biodiversity and promote sustainable land use practices.
Reforestation: Reforestation efforts in the Mindoro Forests involve planting trees and restoring degraded forests.
Wildlife Rehabilitation: Wildlife rehabilitation efforts in the Mindoro Forests involve rescuing and rehabilitating injured or orphaned animals.

Future Directions for Research and Conservation of Mindoro Forests
The Mindoro Forests is a priority site for conservation efforts. In this section, we will explore the various conservation efforts underway in the Mindoro Forests. Including protected areas, community-based conservation programs, and reforestation efforts.

Research Opportunities
One significant area of future research is investigating the complex relationships between Mindoro’s endangered species and their habitats. By understanding the ecological dynamics at play, researchers can develop effective conservation strategies that protect the forest’s biodiversity. Researching the impacts of habitat destruction, climate change, and hunting on the endangered and endemic species of the Mindoro forests can provide valuable insight into the challenges faced by conservationists.
Education and Awareness Campaigns
Another essential area for the future conservation of Mindoro forests is educating the public and raising awareness about the importance of the forest’s biodiversity. Education and awareness campaigns can inspire people to take action to conserve the forest’s unique life forms. By increasing public support, we can create a more significant collective effort to protect these precious ecosystems.
Legislative and Policy Measures
Another way to ensure the conservation of Mindoro forests is to implement legal and policy measures to protect them. Policies can range from the protection of forests and habitats to outright bans on hunting and logging. Establishing protected areas and strict guidelines for resource use is essential to prevent habitat destruction and preserve biodiversity in the forest.

In conclusion
The Mindoro Forests in the Philippines is a unique and valuable ecosystem that is home to an array of plant and animal species, many of which are endemic to the region. Despite these high levels of biodiversity and endemism, the forest is under threat from deforestation, hunting, climate change, and other forms of habitat destruction.
In order to protect this precious ecosystem, a variety of conservation efforts must be implemented, including protected areas, community-based conservation programs, reforestation efforts, education and awareness campaigns, and legislative and policy measures. With the concerted effort of both local and international organizations, we can ensure that the Mindoro Forests remains a refuge for its endemic species and a source of great natural beauty.








